A project is a complete entity consisting of various components, factors, and processes, and each of them needs to be approached in a specific manner to derive meaning and achieve project success. That is where project management methodologies come into play.
Finding a project management methodology that aligns with your needs often means hours of scrolling and wandering through the different corners of the Internet, with a very frustrating possibility of not finding what you truly need.
But don’t worry! We’re here to help you by providing you with a complete guide to understanding project management methodologies. That’s not all, though—we’ll also show you how to choose the most suitable one with ease! Let’s start.
What is a Project Management Methodology?
A project management methodology refers to a well-defined set of principles, tools, and techniques to effectively plan, execute, and oversee projects.
Project management methodologies serve to guide managers to lead their teams, manage tasks, foster collaboration among team members, and get work done. Essentially, they help successfully carry out a project from beginning to end.
Thoughts and learnings about project management approaches have evolved alongside the progress of human consciousness, education, and the development of new technologies, professions, and industries.
This change factor has put almost everyone to the test regarding adaptability to emerging circumstances, which is why we have numerous project management methodologies.
10 Project Management Methodologies to Choose From
To help you understand each of the project management methodologies better, we prepared a list of the top 10 most common ones in the section below.
Whether you’re about to start a project or already in its execution, there is always time to apply new work methods and strive for project success. Let’s see the features of the most prevalent project management methodologies and their most effective characteristics.
#1. Agile Methodology
The Agile methodology was developed in 2001 when the Agile Manifesto was published, containing 12 principles that form the foundation of Agile methodology. It is a project management approach that emphasizes greater flexibility and adaptability compared to traditional methods.
So, what does it look like to complete a project successfully through Agile methodology?
Communication among team members, project managers, project owners, stakeholders, and customers is key. Feedback provided by customers and stakeholders is of significant importance since the project team uses it to plan and take further actions to improve the product or service.
That leads to a greater focus on working software than extensive documentation, enabling a continuous project life cycle. For an effective project life cycle and implementation of Agile methodology, you should consider the following phases:
- Identifying and analyzing project requirements by the project team
- Assigning tasks to the project team
- Working on tasks through iterations or sprints
- Testing the product or service
- Maintaining product or service quality
- Retirement of the software
Agile methodology is a good choice for projects with evolving requirements, innovative projects, and cross-functional teams, to name a few.
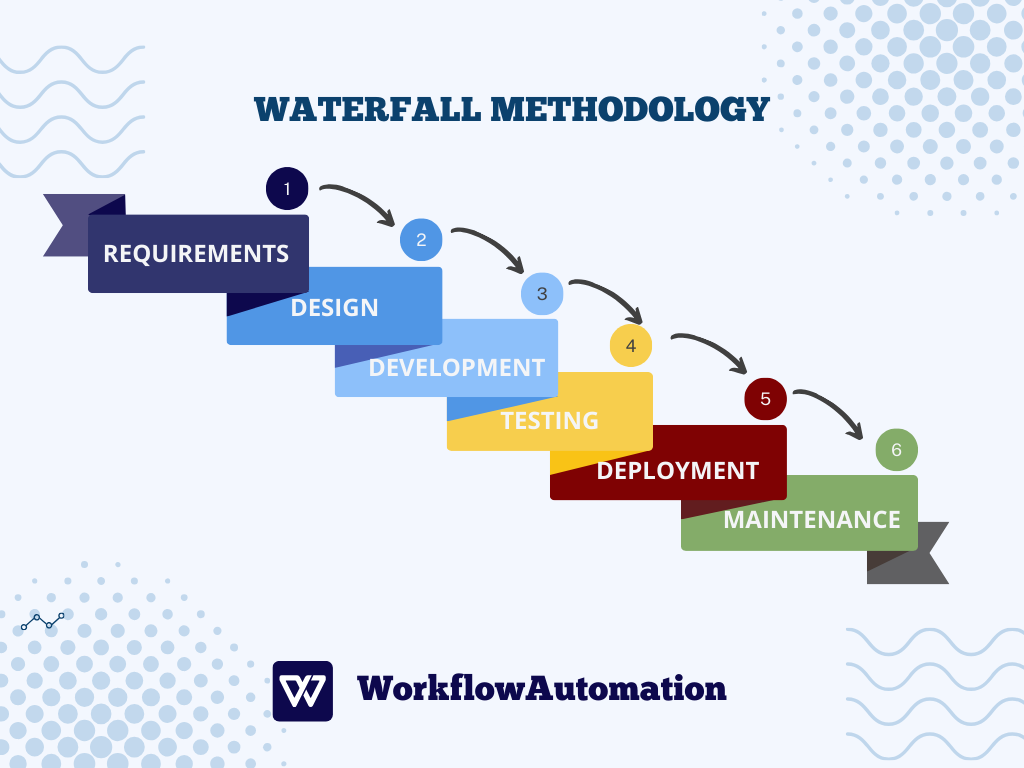
#2. Waterfall Methodology
Making a project management methodologies comparison is often necessary to gain a thorough understanding of how each of them works. For example, when it comes to Waterfall vs. Agile methodologies, we can say the Waterfall methodology reflects a linear progression from the beginning to the end of the project, characterized by strict planning, detailed documentation, and sequential task execution.
Therefore, the Waterfall methodology is an example of a classic approach in project management, which has a name for how to approach project realization. Specifically, the next phase can’t start while the previous one is not fully completed, leaving little space for improvisation and flexibility.
Also, the Waterfall methodology relies on detailed preparation at the beginning of the project, which involves documenting all relevant data, defining a changeable timeline, precise role allocation, and rare consultation with customers.
The Waterfall methodology consists of the following stages:
- Detailed elaboration of project requirements at the beginning of the project
- Creation of a solution for the problem
- Solution implementation
- Testing of the solution
- Product (solution) deployment and maintenance
Waterfall methodology is used by project managers working on projects where all the requirements and tasks are predefined.
#3. Scrum Methodology
Scrum is an Agile methodology framework widely used in software development and other industries, and it’s known for its iterative and collaborative approach. It encompasses four key stages that provide a seamless flow throughout the project lifecycle.
The first stage is the sprint planning meeting, where the Scrum master and product owner gather to define the goals and select items from the product backlog. This meeting sets the foundation for the upcoming sprint and ensures a shared understanding of the project’s direction.
Next, progress tracking takes place during the sprint. Daily scrum meetings enable team members to synchronize their efforts, discuss progress, and identify obstacles. This continuous communication promotes transparency and allows for timely adjustments to optimize productivity.
At the end of each sprint, the sprint review occurs, allowing the scrum team to showcase the completed work to stakeholders. Feedback is gathered, enabling the team to learn and adapt for future iterations. This feedback loop fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
Lastly, release planning involves determining the release of the product or project. The scrum team, product owner, and stakeholders collaborate to assess priorities, plan subsequent sprints, and align them with the project roadmap.
Following these four stages, Scrum promotes a smooth workflow, fosters collaboration, and drives successful project outcomes.
#4. Kanban Methodology
The Kanban methodology originated from the primary goal of engineers, such as Taiichi Ohno, in the automotive industry, specifically Toyota, to increase efficiency and productivity. The Kanban methodology aims to provide a simple yet effective working method.
So, the fundamental principle of Kanban is to utilize a pull system where tasks are added to the workflow only when there is sufficient capacity to complete and deliver them. That helps avoid overloading, bottlenecks, and resource waste.
Central to the Kanban methodology is the use of Kanban boards, which serve as a visual representation of the work process. These boards consist of columns representing the different stages or statuses of tasks. By visually representing tasks in this way, it becomes easier to coordinate and manage work, ensuring a streamlined workflow.
The visual nature of Kanban enables easy monitoring of activities, quick identification of bottlenecks, and efficient problem-solving. Continuous improvement is also an integral part of the methodology, allowing teams to refine and optimize their processes over time.
Despite its traditional roots, Kanban is highly adaptable and applicable across various industries. It allows for implementation within hierarchical structures and suits organizations transitioning to an Agile approach.
Its flexibility makes it suitable for dynamic business as it easily accommodates new changes by addressing priority demands and incorporating them into the planned work scope. This approach ensures uninterrupted workflow between the stages.
To summarize, the main features of the Kanban methodology are:
- Visualized workflow
- Continuous flow
- Pull system
- Limited work in progress
- Adaptability
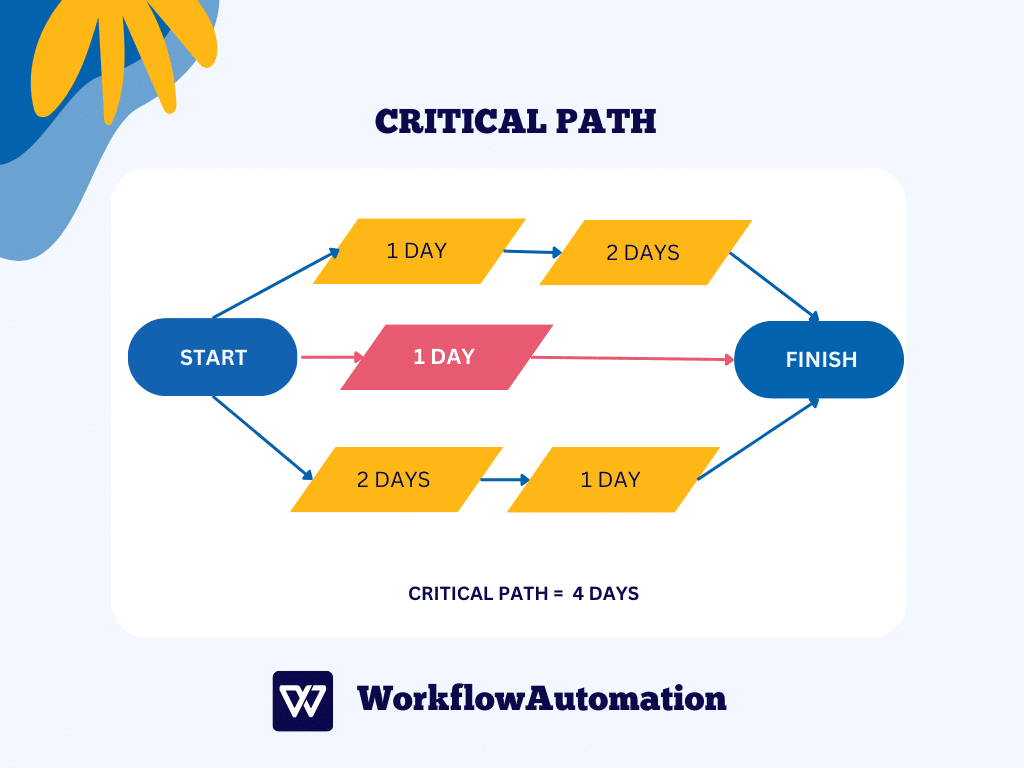
#5. Critical Path Method
The critical path method (CPM) fundamentally involves structuring a project by breaking it down into smaller components. Project managers undertake this approach to ensure proper organization and prevent poor project execution.
This methodology, like Kanban, emphasizes visual representation. However, unlike Kanban, CPM is more complex and suitable for projects with numerous interconnected activities.
Diagrams are used to achieve visual representation, outlining the critical path that represents key moments or milestones, indicating the project’s progress in the right direction and completion.
Identifying these milestones also involves assigning specific time frames and specifying the latest possible completion dates for these milestones. This time determination considers the shortest and longest possible durations to identify an activity’s maximum duration without causing delays or disruptions to task dependencies.
#6. Scrumban
Scrumban combines two project management frameworks, Scrum and Kanban, integrating key features from both frameworks. This combination allows organizations to implement a new way of working more easily and quickly, leveraging the best benefits from both frameworks.
Here’s how it combines the main characteristics:
From Kanban:
- Boards: Used for visualizing tasks and ensuring workflow management.
- No team roles: Easy to implement and flexible.
From Scrum:
- Sprints: Planning tasks through backlogs and setting monthly or shorter-term goals.
- Daily meeting: Regular communication and information exchange about completed tasks and upcoming work to foster teamwork, collaboration, and transparency.
This methodology is beneficial for transitioning systems from a traditional approach to an Agile one. That’s because Kanban provides greater flexibility in work due to the absence of predefined roles, allowing teams to self-organize and focus on continuous delivery.
On the other hand, the team becomes more focused and accountable by introducing Scrum and iterations that imply setting deadlines and work scope before the start of each sprint.
By combining the strengths of Scrum and Kanban, Scrumban provides a balanced approach that suits organizations in transition, fostering adaptability, teamwork, and improved project delivery.
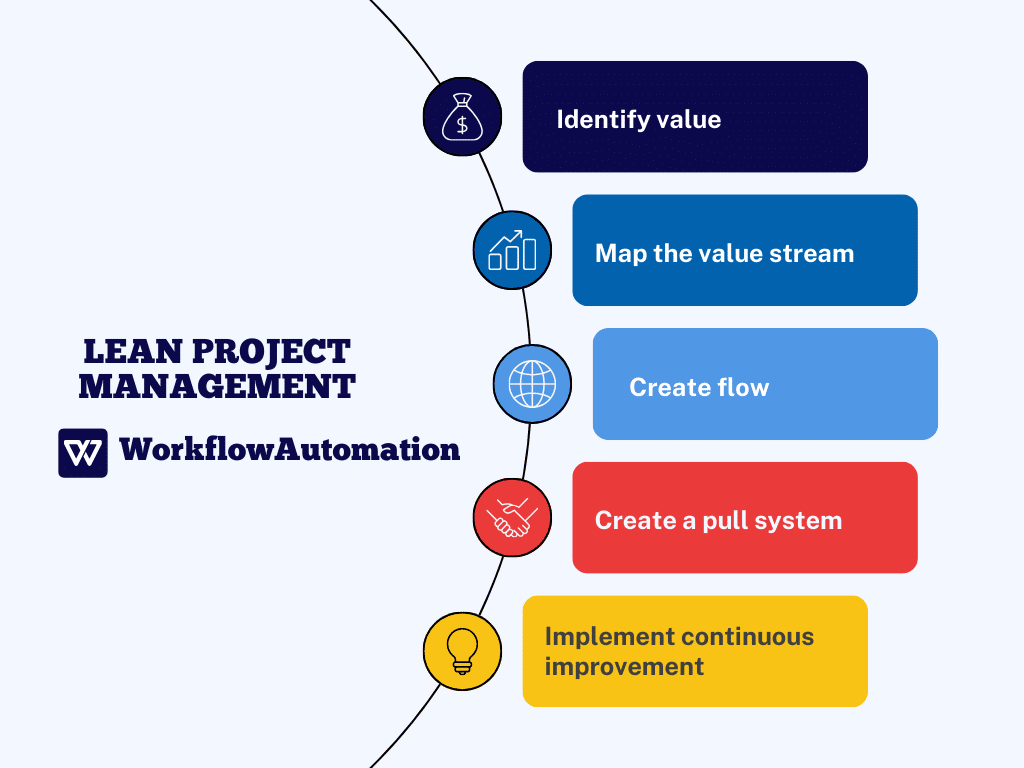
#7. Lean Methodology
Lean methodology focuses on continuous improvement by eliminating waste and enhancing efficiency in production processes and product quality. The benefits of Lean methodology include reduced lead time, cost reduction, and improved productivity and quality.
Lean methodology lies in five fundamental principles that guide it toward achieving efficient and effective processes:
- Identify value by analyzing customer needs, expectations, and desires.
- Map the entire production process comprehensively.
- Create flow, which allows the elimination of bottlenecks and interruptions within the work process, ensuring a continuous workflow.
- Produce the exact quantity of products based on customer demand.
- Foster a culture of innovation, problem-solving, and learning among all employees.
#8. Prince2
Prince2 is a project management methodology that originated in the UK in the late 1980s. Its formal organizational structure characterizes it through clearly defined team roles, processes, and work stages.
The methodology ensures project execution and meeting requirements align with the company’s strategic objectives. As a result, it constantly reviews procedures, analyzes costs and potential risks, and makes informed decisions to deliver valuable products.
However, the formalism of Prince2 and insistence on documenting and recording all actions and decisions can burden the project implementation itself. The excessive focus on process organization and role allocation may overshadow individual creativity and flexibility as well.
On the flip side, this documentation is a valuable resource and provides templates for future work.
Prince2 is suitable for organizations that operate in structured and controlled conditions, such as the medical sector, government, or construction. For small or simpler projects, excessive documentation and formalism may unnecessarily burden the project and reduce efficiency.
#9. Six Sigma
The main goal and foundation of the Six Sigma project management methodology are to increase efficiency and quality while minimizing costs. This approach involves utilizing data collection and statistical analysis to develop strategies that achieve cost savings while delivering superior, successful, and high-quality outputs.
However, this working model can delay project timelines for projects requiring timely delivery as it can take time to collect and analyze data and implement new strategies. Implementing new ways of working, the so-called ‘’problem-solving’’ approach, requires training workshops, resource acquisition, and tools investment.
Due to its focus on quality control and process optimization, organizations commonly apply Six Sigma in manufacturing and production industries where quality control and process optimization are crucial.
However, it can also benefit service-oriented organizations aiming to improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. In addition to increasing efficiency, quality, and cost savings, another significant benefit of this methodology is encouraging collaboration among employees.
It values and promotes the exchange of experiences and knowledge, leading to greater work efficiency by leveraging different perspectives and connecting experiences from various business areas and opinions.
#10. Five Ws (5W1H)
The Five Ws (5W1H) method stands out within project management methodologies as a flexible tool that integrates various methodologies rather than existing independently.
It involves asking the five questions—Who, What, When, Where, Why—to gather information about the project’s purpose, scope, timeline, resources, and stakeholders. This methodology provides a structured approach to understanding and defining project objectives and requirements.
It offers a comprehensive view of the project and its key points, enabling effective responses to stakeholder needs and organizing activities and tasks accordingly.
The Five Ws (5W1H) is commonly used to enhance project planning, align the plan with the project’s initial vision, establish a project roadmap, and is often employed alongside other project management methodologies.
Unlike methodologies that change organizational mindset and habits, the Five W’s (5W1H) serves as a method that promotes work efficiency and complements different project management methodologies.
How to Choose the Right Methodology
When choosing the right project management methodology, organizations should consider key criteria aligning with their needs and characteristics. By evaluating these factors, selecting the most appropriate methodology becomes clearer.
Here are some factors to consider:
- Industry: Different industries have unique requirements and project characteristics. For example, construction and engineering projects can benefit from methodologies like Prince2, focusing on risk management and governance.
Agile methodologies like Scrum or Kanban are more suitable in software development due to their iterative and adaptive nature, allowing for proposing innovative solutions and implementing changes easily.
- Company Size: Larger organizations with established processes and hierarchical structures can find methodologies like Prince2 beneficial due to their structured approach to project management.
On the other hand, smaller companies or startups can find Agile methodologies more suitable as they offer flexibility, quick iterations, and frequent customer feedback, allowing for adaptability and responsiveness.
- Project Complexity: Projects with fixed deadlines and strict requirements may not be the best fit for Agile methodologies like Scrum or Lean, which thrive on adapting to evolving needs and requirements. In such cases, approaches that provide a more structured and predictable approach may be more suitable.
- Team and Organizational Culture: Some methodologies require a high degree of documentation and formalized processes, making them suitable for organizations with a hierarchical and rule-oriented culture. Other approaches prioritize collaboration and self-organization, making them a better fit for teams that value flexibility, creativity, and autonomy.
Conclusion
Deciding on a project management methodology is a challenging task. It requires a thorough analysis of the project and its goals, the resources at your disposal, the employees’ capabilities to carry out the project to completion, and other factors.
Each project management has its characteristics that are universal or tailored to specific kinds of projects and industries. However, you have a sufficient number of options on the table, and we are confident that you can find one that will suit your style, your employees, and the project.
At the end of the day, it all comes down to your desire and the desire of your team to adhere to the basic principles that are more or less the same for all methodologies and to fulfill the set goals through quality work and complete the project.