The Critical Path Method (CPM) is one of the classic project management methodologies. The journey from the initial idea to project completion involves numerous phases, role distributions, responsibilities, and leadership.
It is precisely in mapping the key segments of the Critical Path Method that its significance comes to the fore because it enables the team to clearly identify the points in the project that largely determine the outcome.
In the following text, we will break down the Critical Path Method into parts and explain each one, giving you a clear understanding of how to reach your desired goal.
Let’s dive in!
What is the Critical Path Method (CPM)
We can say that the project management industry changed for the better when it adopted this methodology that originated in the 1950s as a highly efficient technique for completing projects.
First, let’s cover the Critical Path Method definition.
The Critical Path Method (CPM) primarily entails focusing on key tasks within a project, without which there simply cannot be a positive project outcome. Of course, all tasks assigned to a team need to be completed, but the critical ones are those where there is no room for compromise.
On the other hand, project managers willingly use CPM because it has been empirically proven that they can easily achieve an effective scope of work, which team members naturally follow.
So, the task of a project manager is to identify which activities are crucial and to explain to their team why they need to adhere to that path, highlighting the benefits it brings.
It is crucial for team members to understand that the only way to achieve the goal by using this methodology involves closely monitoring and following the established timeline and adhering to individual deadlines for each task.
Importance of Critical Path Method
CPM allows for a complete insight into project management and the team regarding all project tasks and when and how they should be executed.
Here, we will highlight the three most important reasons why the CPM process is considered a crucial segment of the project management workflow:
- Critical activities. Breaking down the project into smaller tasks and assigning priorities enables the project team to have a clear picture of which tasks are crucial. This will allow them to allocate their creativity and avoid spending their energy and effort on tasks that cannot be categorized as “crucial.”
- Time. Smart allocation of time required for each important task cannot but result in overall team efficiency and, consequently, project schedule efficiency. On the other hand, it will save time that can be used for other secondary activities.
- Cost. If you save time, you will also save money. That is why implementing the Critical Path Method ensures cost savings, especially when it comes to avoiding expenses that can arise from secondary tasks in the project.
When Should You Use the Critical Path Method?
You should use the Critical Path Method for complex projects since this methodology breaks down a project into smaller components or tasks and assigns deadlines for their completion.
Complex projects typically last 2 or 3 years and require the completion of numerous activities within that time frame. They are characteristic in construction, product development, medicine testing, and similar fields.
Let’s consider the construction of a student campus as an example. It involves performing legal tasks related to contracts and permits, executing tasks for the architecture and construction teams, procuring materials, and carrying out various technical works. These tasks represent the project’s key tasks, and each has a specific deadline.
How to Use the Critical Path Method
Once we have defined what it is, its significance, and when to use the critical path method, it remains to clarify the steps involved in this method with some critical path method examples.
This project management technique will help you identify primary and secondary activities, understand the relationships between all activities, and enable you to easily track your activities by determining the time required for each.
#1. Identify the Activities
First and foremost, when faced with a specific project and a defined goal, in order to avoid getting lost and wandering off track, it is necessary to divide your project into stages or activities. Determine all the activities that need to be performed in order to complete the project.
For example, if you are tasked with writing a paper (academic or scientific), initially, you only have a topic. To address the given topic in your paper, you need to cover various areas related to it. This can be achieved by breaking down the given topic into essential segments or components, which will provide you with the framework for what you need to write.
#2. Identify the Dependencies
Once you have listed all the activities required for your project, it is important to determine the relationships or dependencies among these activities. Identifying activity dependencies will further assist in prioritizing them, determining the sequence in which they should be executed, and distinguishing between main and subsidiary activities.
For instance, you need to identify activities that need to be started or finished until another activity is completed or initiated. Additionally, you should identify activities that can be performed in parallel or completed simultaneously.
Recognizing the dependencies among activities is crucial because the completion of the entire project depends on the smooth functioning of each individual activity.
#3. Design a Network Diagram
Network diagrams help you visually understand all the activities involved in a project, along with their dependencies.
By using diagrams, you gain a clear overview of the initial activities, their start times, and expected durations, and as the project progresses, you can visually track the workflow and see how activities are being executed.
This allows you to monitor whether activities are being completed within the scheduled time or if there are any delays.
You can design network diagrams using various techniques and tools. One approach is to create the diagrams yourself, using different symbols and labels.
For example, you can use rectangles to represent upcoming activities and different colors to indicate their relative importance. Arrows can be used to illustrate the connections and dependencies between activities.
There are also software tools available, such as Microsoft Project, that provide templates and features specifically designed for creating network diagrams. These tools make it easier to create and update the diagram as the project progresses, as they often offer built-in functionalities for managing tasks, dependencies, and timelines.
#4. Estimate Activity Duration
A well-executed project requires a good plan, and part of that plan is determining the time required to complete each planned activity. Therefore, it is necessary to estimate the duration of each activity.
This step is crucial because the completion of activities determines the project’s overall timeline, and in order to maintain a smooth workflow, it is important to realistically plan the execution time for each activity.
To estimate activity duration, you can utilize various indicators. These indicators may include theoretical calculations, past experience, and statistical data. By considering these factors, you can arrive at a reasonable estimate of the time required for each activity.
It is important to note that the estimated duration should neither be overly optimistic nor excessively conservative. It should be a realistic average that takes into account potential unforeseen circumstances or delays that may arise during the execution of activities.
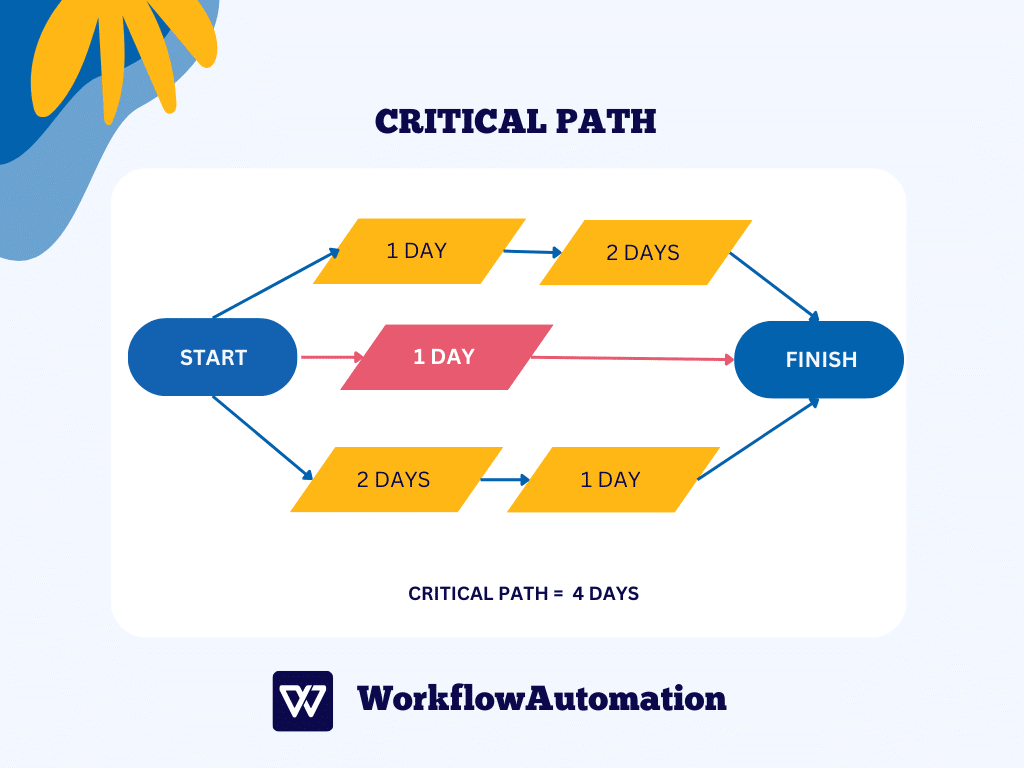
#5. Calculate the Critical Path
To calculate the critical path, you need to determine the longest series of interdependent activities that, if not completed on time, would cause project delays.
First, you must calculate the individual durations of all interdependent activities, considering their earliest possible starts and earliest possible completions.
Next, you need to determine the execution of these activities, with their latest possible starts and latest possible completions.
By doing so, you can identify the specific time at which interdependent activities, crucial for project completion, can start or finish at the latest, both individually and in their interdependencies. This analysis is crucial to preventing project delays.
#6. Determine the Floats
Determining the floats helps identify the flexibility in scheduling non-critical activities without impacting the project timeline. Float, also known as “slack,” represents the amount of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the overall project’s completion.
To calculate the float for identified activities, we consider two values: the earliest start time (ES) and the latest start time (LS). The float (F) is then determined when you simply subtract the ES from the LS:
Float (F) = LS – ES
If the float value is zero, it indicates that the activity is critical, and any delay will directly impact the overall project timeline. Conversely, a float value greater than zero signifies that the activity can be delayed without affecting the project’s completion.
Critical Path Method vs. Gantt Chart
The Gantt chart is also a project management tool used for tracking your project, providing you with a visual overview of your activities and how they progress. In a Gantt chart, activities are typically listed on the left side, while you track their execution on the other side.
The chart represents the timeline of these activities, indicating when they start, how long they will take, and when they finish. Within the Gantt chart, various options exist, such as using different symbols to mark important elements like project milestones or activity dependencies.
Additionally, you can use different colors to represent different project phases. All of these features facilitate a clear view of the project’s status.
On the other hand, the Critical Path Method (CPM) provides insight into the overall project duration by considering the individual shortest and longest durations of activities, as well as their interrelationships and dependencies.
The goal is to identify the critical path—the series of steps whose disruption would have the greatest effect on the project’s schedule.
Critical Path Method vs. PERT
Although both techniques aim to achieve results in the shortest possible time, there are some key differences between these two methods.
PERT primarily represents a visual project management method, while CPM is a statistical method.
For projects without precisely defined durations, PERT is more suitable. It allows you to analyze activities and estimate the time required for their completion before the project starts, focusing primarily on organizing activities, planning, coordination, and management.
On the other hand, the critical path method focuses more on executing all the necessary activities within a given timeframe to ensure the successful completion of the project.
Conclusion
The Critical Path Method can make that complex project look much more manageable.
By identifying key activities and allocating the required time for each of these critical points, the project management team can ensure an efficient project schedule.
On the other hand, team members who work on the project on a daily basis will be able to concentrate more easily on what is important, ultimately resulting in a flow that will benefit everyone on the team.